By integrating high-precision traffic planning with the building-specification operation plan, Toshiba offers you an optimum elevator group control system for your building.
This system will corresponds to the demand by distinguishing the peak hours such as early of working hours and lunch time from the non-peak hours. The latest elevator group control system allows multiple elevators to work together systematically and optimally while providing maximum conveniences to the passengers.
1. Deciding speed
Speed of elevator is generally determined by the number of floor in the building. A general guide is that it should not take more than 30 seconds to travel in between the top and the lowest floors. Decide the optimum speed for the building by applying this basic rule and considering the factors such as building's purpose, characteristics, and service policy.
■ Relationship between elevator speed and number of floors in building
 |
 |
2. Deciding number of cars
1). Determine the number of cars required
Decide sufficient number of cars to maintain the transportation capacity and waiting time within the service standards during peak hours which has large number of passengers. Below is a general guideline to determine the number of cars.
| Service Level | Office Building | Hotel |
|---|---|---|
| Number of users per elavator car | Number of rooms per elavator car | |
| Service oriented |
150 - 200passengers |
90 - 120rooms |
| Standard service |
200 - 250passengers |
120 - 150rooms |
| Economy oriented |
250 - 300passengers |
150 - 180rooms |
Note that for hotel, approximately two-thirds additional cars need to be allowed as service elevators are not included.
2). Traffic calculation
When deciding on the number of elevator cars, passenger capacity and service floors, study of numerical data is required for the traffic calculation. The general values for traffic calculation are shown below.
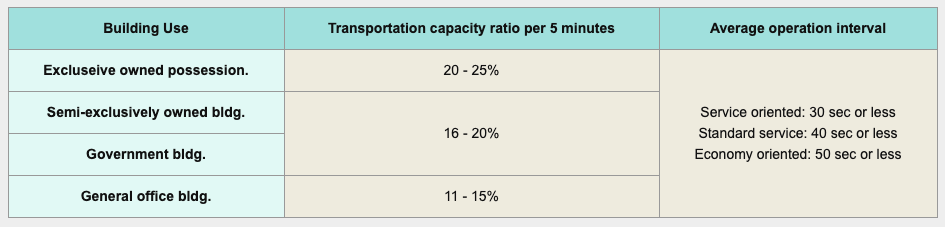
Office building :
Start of office hours set to be peak for traffic demand
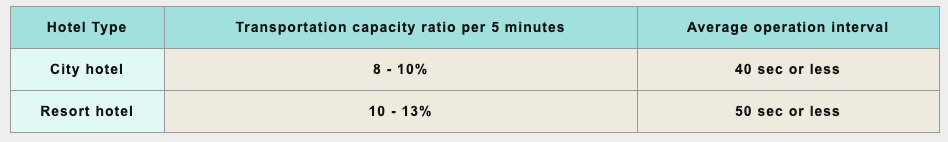
Hotel :
Morning hours for check-ins and evening hours when guests leave or go to dinner set to be peak for traffic demand
3). Simulation
The building's traffic demand could be simulated with computer to understand more about the service condition such as average waiting time and chances of long waits. Integrating the result simulation with the traffic calculation to allow for better accuracy planning. The output of the simulation contains the peak hours and the usual service condition. The general values for the simulation are as follows:
Example : Rental office building with demand concentration at 6% of building population per 5 minutes span (during office hours)
Average wait times : 30sec or less
Chance of response within 30seconds : 70% or greater
Chance of response after 60 seconds or more : 5% or less
3. Deciding Passenger Capacity
Decision of passenger capacity must be planned with the considerations of peak hours , characteristics of building and make allowance for leeway. Generally, the following plans are recommended:
-
For a small or mid-sized building, passenger capacity of 15 (load capacity of 1000kg) or higher.
For a hotel or large office building, passenger capacity of 24 (load capacity of 1600kg) or higher. -
Doors should open from the center, and the car entrance should be as wide as possible.
-
The car should be with in relation to its depth
4. Deciding Service Floor
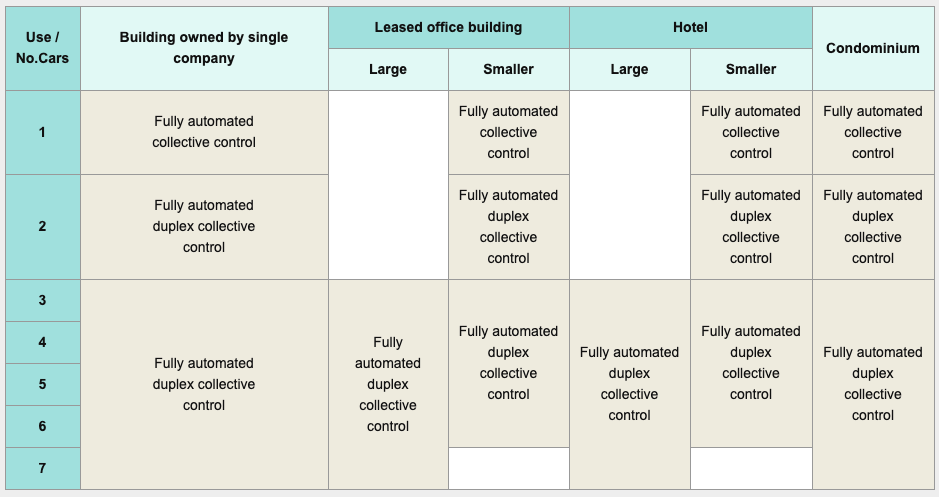
Office buildings of more than 20 stories are zoned in order to decrease transportation time and improve the rental rates. Zoning refers to dividing elevator service into several zones, and assign group of elevators for each zone. The following point must be take into consideration in order to apply the zone system effectively.
Unlike office buildings, a single elevator group is recommended for hotels 40 stories or less to give priority to the first-time users and conveniences. Using a single group elevators, make less hassle for the passengers to select an elevator based on their destination floor, and is also more flexible than zoning. Allow a number of elevators to be used for special occasions temporarily, without greatly affecting the passengers. In additional, if the hotel has banquet halls or wedding chapel, it is advisable to assign escalator or elevator specially for these guests.
 |
|
5. Deciding The Layout
Elevator layout has great influences on building's functionality. Thus, the elevator must be installed in such a way that it is easy to use without affecting the performances.
Recommend the examples of elevator layout
 |
 |
 |
-
Position the elevator so that any part of the floor can be reached with little walking, with a focus on lines of movement for traffic.
-
When installing several elevator groups, concentrate each group in a single location.
-
When lining elevators in a row, keep the number of elevators to no more than 4, with at most 8 meters between the elevators on each end.
-
If more than 4 elevators are installed, place them on facing sides of a hallway, with 3.5 to 4.5 meters between them.
-
It must be possible to see all elevators from anywhere in the hall. Avoid constructions with pillars in the elevator hall, and layouts with recessed elevator car entrances.
-
The elevator hall must be large enough that passengers do not spill out even during peak hours. In general, plan the elevator hall large enough to hold about 1/2 the combined maximum capacity of the cars (about 0.5 to 0.8 m2 are required per passenger).
6. Operating system
Select the operating system based on the building functionality, number of elevators in group.
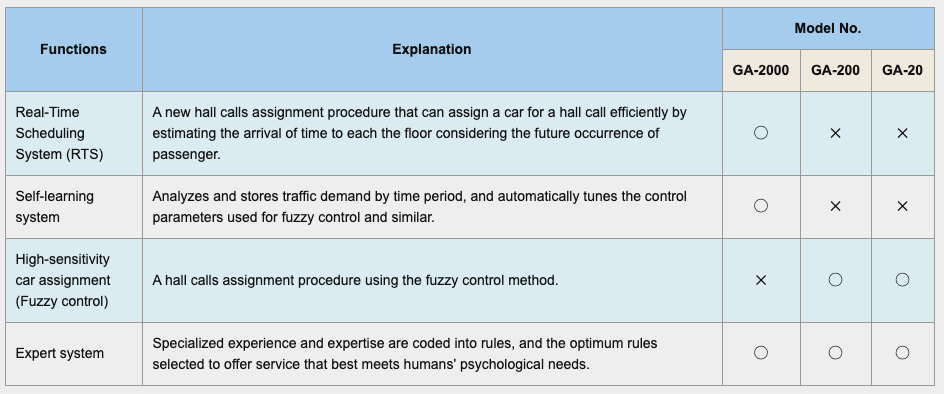
7. GROUP CONTROL SYSTEMS
We will always analyze the very latest elevator operating conditions to predict the future elevator service situation, select the most suitable elevator and deliver it to the point of use.
Toshiba Elevator Group Control System: The Real-Time Scheduling System (RTS) not only shortens the waiting time of the elevator but also allows us to provide various environmentally friendly driving functions such as "Power saving function" and "Power saving allocation function".
◯:STANDARD △:OPTIONAL ✕:Inapplicable specifications
| Descriptions | Number of elevator application | Number of the maximum application floors (Note1) | Model No. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA-2000 | GA-200 | GA-20 | |||
|
"Real time scheduling system (RTS)" can be applied to 12 elevators maximum with the latest features such as "Power saving function" and "Power saving allocation function". |
3 to 12 units |
128 stops |
◯ |
|
|
|
It is a group control system applicable for medium and small sized buildings capable of up to 6 elevators, taking over the design concept of the top model of the group control systems. |
3 to 6 units |
64 stops |
|
◯ |
|
|
This is a group control system for medium and small sized buildings that meet the specifications of basic functions such as "Fuzzy control " and high-sensitivity allocation to shorten elevator latency. |
3 and 4 units |
40 stops |
|
|
◯ |
※Note 1: An express zone is not included. The actual number of applications is based on each elevator models .